4G made it possible for ridesharing apps like Uber and Lyft to develop. A ridesharing car that drives itself – without any human assistance – may be possible one day with 5G. In addition to autonomous cars, 5G is a network that is being rolled out steadily throughout the United States and other countries worldwide.
Businesses are competing to get the most advanced and fastest 5G networks. Experts anticipate the many revolutionary innovations that will be built on top of 5G to make it the most competitive technology in the world. It will still take time for wireless customers to see the major benefits that 5G could one day bring. In addition to smart cities, remote surgeries, and automated factories, the network is essential to enabling new technologies.
Though there are many differences, three main differences between 5G and 4G include speed, bandwidth and “latency.” Latency refers to the time it takes between devices to communicate with the server. Those perks, however, are going to be contingent on investing billions in new infrastructure.
Many providers have already considered and integrated this new technology. For instance Optimum Altice. Altice Mobile combines the country’s leading wireless networks with Altice’s own network infrastructure and fiber optics to offer our customers fast, reliable, and flexible LTE. New wireless technologies such as 5G will also be integrated into Altice Mobile in the near future.
With that, let us get to the key differences between 4G and 5G.
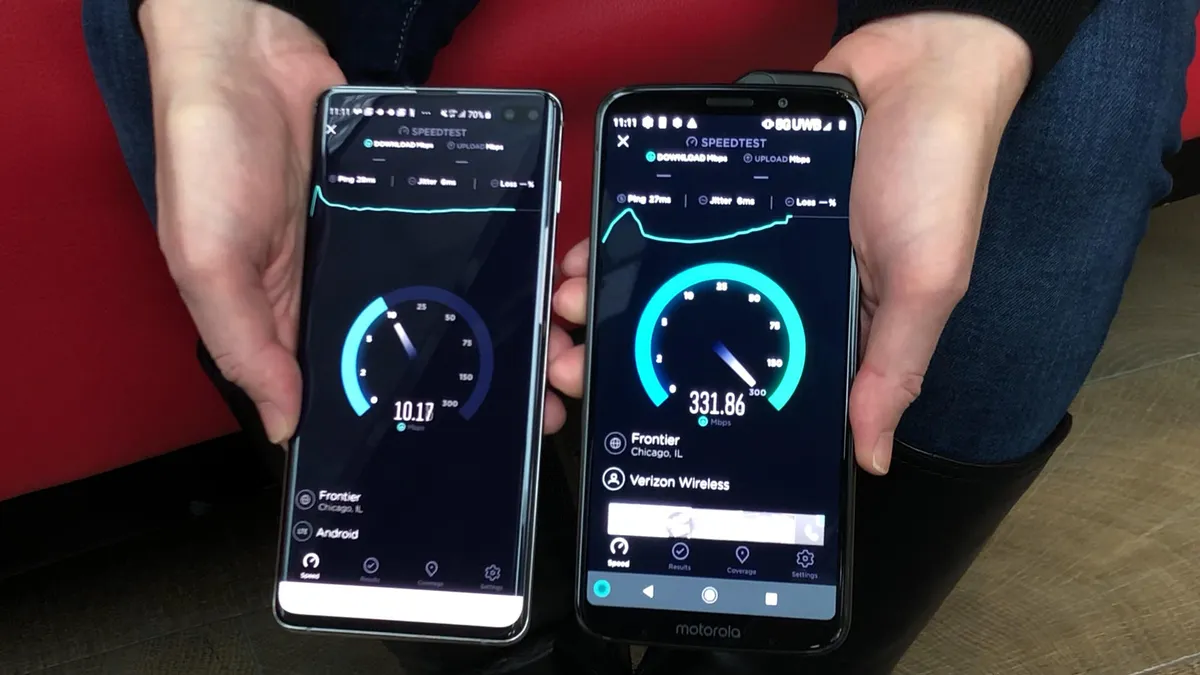
Speed
This is another element of the next-generation network that is eagerly awaited.
The next-generation network will offer speeds that are 100 times faster than 4G. A two-hour movie could be downloaded in less than 10 seconds at such speeds (no more panic on the tarmac as you download your in-flight entertainment).
Consumers will be able to stream movies and download apps with fast speeds, but they’ll be needed in a multitude of other areas as well. Manufacturers talk about putting video cameras throughout factories so they can analyze large amounts of video footage in real time to monitor the quality of their products.
High-band spectrum is a super-high-frequency airwave that most 5G networks use to deliver these speeds. Data is transmitted faster with the higher frequencies than with the lower frequencies in 4G.
The high-band spectrum is not very efficient and is not able to penetrate walls, windows, lampposts, and other solid surfaces very easily. This isn’t very convenient when we want to keep working our tiny computers as we walk from the subway station, across the street, and into the office.
Those challenges have led to wireless carriers installing thousands of small on light poles, towers, walls and often in close vicinity to one another. Because of this, most carriers are rolling out 5G city by city – for the network to function, the city must have plenty of small cells.
In addition, many buildings will be equipped with their own 5G cell sites to ensure the network works. Wow! That does sound cool!
Capacity
When there are a lot of people gathered in a relatively small space – a concert, a sports stadium, the airport during the holiday travel season – and you see a “spinning wheel of death” when trying to open a webpage or watch an Instagram video, it can be very frustrating.
Congestion can result if there are too many devices trying to use the network at the same time. Due to a large number of devices, the network infrastructure cannot handle the data traffic, resulting in slower download speeds and longer lag times.
5G technology is expected to solve this issue and more. A significantly larger network capacity is expected than that of 4G. In addition to a better connection for everyone’s phones, you will also be able to post about your big game experience on social media more easily. Many, many more devices can be connected to the network as a result.
There are more lanes for more cars to drive on the 5G network, which is like a new and improved freeway. In addition to increased bandwidth, this element of the update would make it possible to connect toothbrushes, kitchen appliances, streetlamps, and more for the era of the “internet of things.”
Latency
It is important to note that there is a small but substantial difference between speed and latency, which is the amount of time it takes for devices to communicate with one another or with the server they are receiving information from.
You can measure the speed of your phone by the time it takes to download a webpage. A friend’s phone registers that a new message has been received after receiving a text message from you. This time is called latency. It is true that latency is measured in milliseconds, but when sending and receiving billions of bits of data per second, such as video – or data from a self-driving car – the milliseconds add up.
5G will virtually eliminate latencies that exist with 4G.
The new technology will be helpful for innovations like remote real-time gaming – allowing people to play the same game from different parts of the world using Internet-connected devices at the same time, no matter where they are.
Self-driving cars, for example, will be unable to navigate by themselves without this information, since they need to send signals about their surroundings to a cloud-based computer, which analyzes the situation and returns the care instructions. That communication needs to be instantaneous for self-driving cars (and their passengers).
Conclusion
Surely the wonders of 4G and 5G are amazing. There are differences between the two, but both have their own benefits. We hope you are now clear about the key differences. We suggest you to use Levo Pa71 Power Bank to charge your device in emergency.
That is all for this post. If you have anything to add to this post, you are more than welcome to do so. Leave your questions and comments in the section below. You can also drop your questions and queries. We will get back to you soon.